Key Kenyan Education Laws 2025/2026
A Clear & Structured Guide for Schools, Teachers, Parents & Education Providers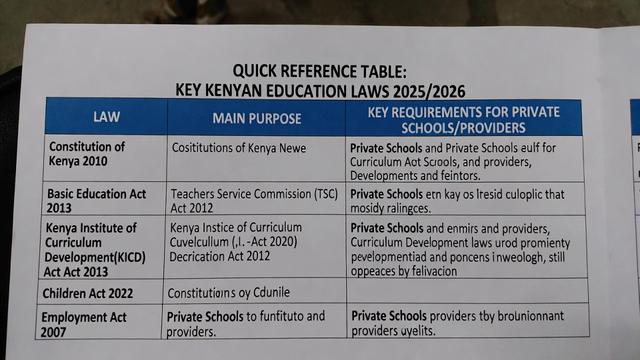
Whether you're running a private school, teaching, placing students, or advising parents, understanding the current legal framework governing education in Kenya is essential.
This article summarizes the most relevant statutes and regulations as of January 2026.
1. The Constitution of Kenya 2010
Foundation of the Right to Education- Article 43(1)(f) – Right to education as a fundamental human right
- Article 53(1)(b) – Every child has the right to free and compulsory basic education (pre-primary, primary & secondary)
- Article 55 – State must ensure access for marginalized groups
2. Basic Education Act No. 14 of 2013 (as amended)
The Main Law for Basic Education (Pre-Primary to Secondary)- Free & compulsory primary and secondary education (government capitation via NEMIS)
- Registration of private schools mandatory (MoE certificate required before opening)
- School Boards of Management (BOMs) mandatory for governance
- Prohibitions – Corporal punishment banned, expulsion only after due process
- Penalties – Operating unregistered school → fine up to KES 1 million or 2 years imprisonment
3. Teachers Service Commission Act No. 20 of 2012
Who Controls Teachers in Kenya?- TSC is the sole body for:
- Registration & licensing of teachers
- Discipline, promotion, transfer
- Code of Conduct & Regulations
- All teachers (public & private) must be TSC-registered
- Unregistered teaching → illegal (fine/imprisonment)
4. Kenya Institute of Curriculum Development Act No. 4 of 2013
Who Approves Curriculum?- KICD develops, reviews, and approves all curricula
- Private & international schools must get KICD approval for non-CBC curricula (e.g., Cambridge/IGCSE, IB, British)
- Unauthorized curriculum → offense
5. Children Act 2022 & Child Protection Laws
Protecting Learners- Mandatory reporting of child abuse by all school staff
- Schools must have child protection policies
- Sexual Offences Act 2006 → severe penalties for abuse in schools
- Work Injury Benefits Act → covers teachers/staff injuries
6. Employment & Labour Laws (Relevant to Schools)
- Employment Act 2007 → written contracts, probation (max 12 months), leave, termination notice
- Labour Relations Act → teachers can join unions (KNUT, KUPPET)
7. Private & International Schools – Extra Rules
- Must be registered with MoE
- International curricula require KICD approval
- Must comply with same child protection, fee transparency, and teacher registration rules
Quick Reference Table – Key Laws at a Glance
| Law / Act | Main Purpose | Key Requirement for Private Schools/Providers |
|---|---|---|
| Constitution 2010 | Right to education | Free & compulsory basic education |
| Basic Education Act 2013 | Registration & governance | MoE registration certificate mandatory |
| TSC Act 2012 | Teacher registration & discipline | All teachers must be TSC-registered |
| KICD Act 2013 | Curriculum approval | Non-CBC curricula need KICD approval |
| Children Act 2022 | Child protection | Mandatory abuse reporting & policies |
| Employment Act 2007 | Employment contracts | Written contracts, probation ≤12 months |
Practical Advice for Education Providers (like ElimuHub)
- Always ensure recruited teachers are TSC-registered
- Use legally reviewed appointment letters (Employment Act compliance)
- Advise private schools on MoE registration & KICD curriculum approval
- Maintain transparency on fees and avoid hidden charges


Comments